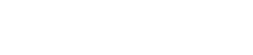ingot mold
Ingot mold is a necessary and revolving bulk ingot equipment for die casting production in steelmaking plants. It has an important impact on the surface and internal quality of ingot mold and the cost of ingot mold. Ingot mold life (times) or ingot mold consumption (kg/t steel) is a major technical and economic indicator of steelmaking production.
Why choose AGICO Cement's ingot molds for steel casting
- We offer customization options based on customer specifications, ensuring molds meet exact shape, weight, and size requirements.
- AGICO Cement has specialized in manufacturing ingot molds for steel casting since its inception. Our focus is on producing molds capable of handling a variety of materials including heat-resistant cast iron, ductile iron, vermicular graphite cast iron, gray cast iron, and cast steel. These molds range in weight from 10 kilograms to 160 tons and are available in different shapes such as integral, split, octagonal, and round molds. They play a crucial role in shaping special steel, supporting iron and steel research, and facilitating aerospace material studies.
- Our manufacturing facilities boast advanced equipment including a 3-ton medium frequency induction furnace, a 10-ton electric furnace, a 20-ton reverberatory furnace equipped with warm air blast technology, a 10-ton warm air blast reverberatory furnace, a 20-ton sand treatment line, and two 100-ton overhead cranes, alongside other heavy-duty pouring and lifting equipment.



- Operating conditions for ingot molds for steel casting are rigorous, subjecting them to temperature differentials, phase transformations, residual stresses, and mechanical strains during use. Over time, these conditions can lead to the development of fine cracks that may compromise mold integrity and functionality.
- Our molds are designed to facilitate strong adhesion between the solidified steel ingot and the mold, minimizing demolding issues. To enhance mold longevity and performance, we employ two main strategies: advanced coatings to improve surface quality and infiltration technology to create metal-ceramic composite surfaces. Ceramic components on mold surfaces resist iron casting oxidation, thereby extending mold lifespan.
- At AGICO Cement, we are committed to delivering high-quality ingot molds for steel casting that meet the diverse needs of our customers while ensuring durability and performance under demanding operational conditions.
Different types of ingot mold
According to the shape of the longitudinal section of the ingot mold, it can be divided into a large upper and a lower part with a thermal insulation cap or a gap hanging insulation board ingot mold, and an upper small and a lower large open or bottle type ingot mold. The former is traditionally used for pouring sedated steel ingot mold, customarily called sedated steel ingot mold, and now it is also used for pouring boiling steel ingot mold, and the latter is traditionally used for pouring boiling steel, traditionally called boiling steel ingot mold, and now It is also widely used for casting killed steel. According to the cross-sectional shape of the ingot mold cavity, it can be divided into square, rectangular, circular and polygonal types. According to the shape of the inner wall of the ingot mold, it can be divided into convex, concave, straight and corrugated.


Pouring method of large ingot mold
1. The ordinary ingot casting method is a method of pouring molten steel into the ingot mold in the atmosphere to make it slowly solidify, which is called the ordinary ingot casting method. It is further divided into the betting method and the betting method. The pouring method of large ingot molds is commonly used. German Thiessen. Henrich Metallurgical Company successfully poured the ingot mold weighing 435t by using the betting method.
The upper injection method is prone to surface pores due to the splash of molten steel. Compared with the betting method, the surface of the ingot mold is more uneven. In order to prevent the secondary oxidation of molten steel during casting, inert gas protection is used.
2. In the vacuum ingot casting method, the molten steel in the ladle is poured into the ingot mold placed in the vacuum chamber through the tundish, which is called the vacuum casting method. The degassing equipment was trickle removal as previously described.
This method is widely used in the production of large ingot molds for the purpose of dehydrogenation. Compared with the ordinary ingot casting method of atmospheric casting, it not only avoids the secondary oxidation of the molten steel, but also reduces the non-metallic inclusions in the molten steel.
At the same time, the carbon-oxygen reaction under high vacuum conditions can be used to control the vacuum carbon deoxidation, which is particularly important for the ingots of low-silicon NiCr-M6, NiCrMoV and other steel grades or ultra-pure steel ingot molds. It not only reduces the material in the steel, improves the purity of the steel, but also significantly improves the segregation of the ingot mold and greatly improves the internal quality of the ingot mold.
The number of edges and corners of the large ingot mold is 8.16.24 and 32. The multi-edge ingot mold shuttle angle is more blunt, the formation of segregation is less, and the angular deviated bridge is scattered because of the more edges. Increasing the number of edges and corners is to increase the number of curved surfaces of the ingot mold, so that there can be greater buffering and space during solidification, and the tendency of crack formation is given. Therefore, extra-large ingot molds mostly use 24 edges or 32 edges. As for ordinary ingot molds, each factory is determined according to the situation of Chao body.



Usage and maintenance of ingot mold
The life of ingot mold is directly related to factors such as material, structure, casting quality, management and use. Establishing a sound and reasonable management system, strengthening the technical management of ingot mold, and achieving correct use, reasonable turnover, and timely repair are important ways to improve ingot mold life and reduce ingot mold consumption. Bake the new ingot mold to 80-120℃ before use. The operation of forming the mold should be lightly lifted and placed, the rising hole should be centered, avoid pouring high-temperature steel, and try to shorten the time from injection to demoulding. Ingot mold should be repaired in time once there are defects such as large cracks, ear drop or inner wall pits and ablation mesh (cracking) during use. Different repair methods can be used according to the damage situation. For longitudinal and transverse cracks, thick steel plate riveting is used to repair the gaps, and the gaps are filled with cast iron electrodes; for the damaged mold ears, cast iron electrodes are used for layer-by-layer surfacing welding or a combination of thick steel plate riveting and welding; the ingot mold after welding can be repaired. Increase the service life by 20 to 30 times. For inner wall defects, a mixed refractory material (such as a mixture of 30% iron powder, 20% refractory mud, 20% graphite powder, 15% chromite and 15% water glass) can be used at a mold temperature of 80 to 120°C. Apply it while it is still hot, and use it 4-5 times after applying it. The damaged ingot mold that cannot be repaired shall be judged to be discarded in due course.